利用CRISPR-CAS9在酵母中构建和分析DNA序列变异文库
| 导读 | High-throughput creation and functional profiling of DNA sequence variant libraries using CRISPR–Cas9 in yeastConstruction and ... |
High-throughput creation and functional profiling of DNA sequence variant libraries using CRISPR–Cas9 in yeast
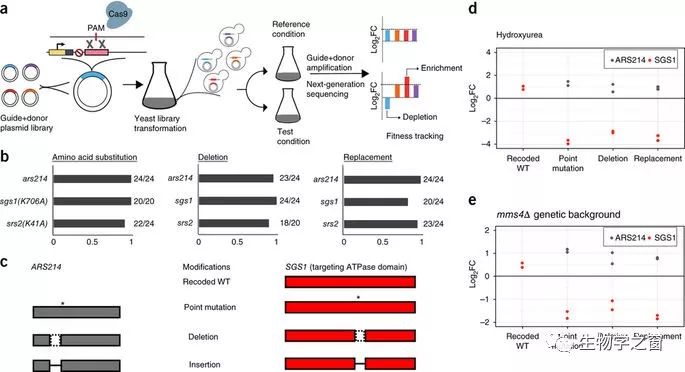
Construction and characterization of large genetic variant libraries is essential for understanding genome function, but remains challenging. Here, we introduce a Cas9-based approach for generating pools of mutants with defined genetic alterations (deletions, substitutions, and insertions) with an efficiency of 80–100% in yeast, along with methods for tracking their fitness en masse. We demonstrate the utility of our approach by characterizing the DNA helicase SGS1 with small tiling deletion mutants that span the length of the protein and a series of point mutations against highly conserved residues in the protein. In addition, we created a genome-wide library targeting 315 poorly characterized small open reading frames (smORFs, <100 amino acids in length) scattered throughout the yeast genome, and assessed which are vital for growth under various environmental conditions. Our strategy allows fundamental biological questions to be investigated in a high-throughput manner with precision.
重点词汇
High-throughput 高通量
variant libraries 变异文库
yeast 酵母
alterations 改变
mutants 突变体
deletions 缺失
substitutions 替换
insertions 插入
en masse 全体
demonstrate 证明
utility 效用
helicase 解旋酶
highly conserved 高度保守的
residues 残基
genome-wide library 全基因组文库
open reading frames 开放阅读框
amino acids 氨基酸
scattered 分散的
vital 至关重要的
investigated 研究
precision 精确
背景知识
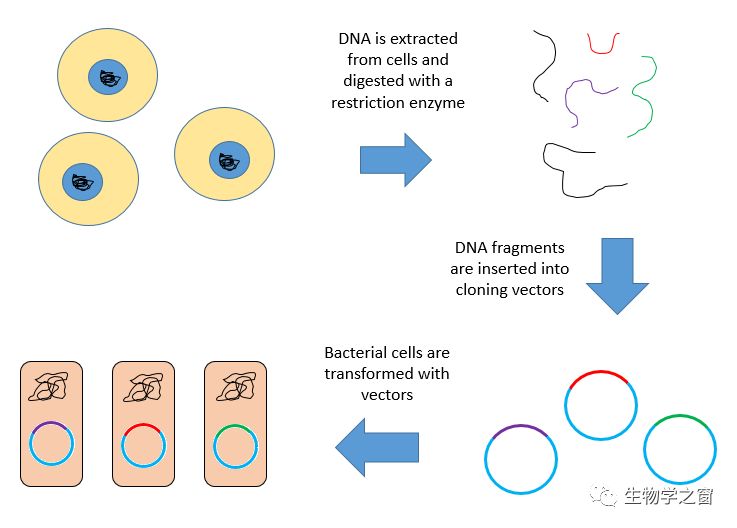
A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism(生物体). The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested(消化) with a restriction enzyme(限制性内切酶) to cut the DNA into fragments(片段) of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase(连接酶). Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification(放大) and retrieval(回收) of specific clones(克隆) from the library for analysis.
There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities(容量). Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.
Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing(测序) applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.(来源:维基百科https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genomic_library)
(转化医学网360zhyx.com)
 腾讯登录
腾讯登录
还没有人评论,赶快抢个沙发