AJHG:发现可引发三种不同疾病的特殊基因
| 导读 |
近日,刊登在国际杂志The American Journal of Human Genetics上的一篇研究论文中,来自西班牙巴塞罗那自治大学、维尔茨堡大学等处的研究者通过研究发现了可以引发三种不同疾病的单一基因。
这项研究中研究者使用了新一代的大规模超深度测序技术对范科尼贫血患者中20,000多个基因进行了测序分析,范科尼贫血(Fancon... |
近日,刊登在国际杂志The American Journal of Human Genetics上的一篇研究论文中,来自西班牙巴塞罗那自治大学、维尔茨堡大学等处的研究者通过研究发现了可以引发三种不同疾病的单一基因。
这项研究中研究者使用了新一代的大规模超深度测序技术对范科尼贫血患者中20,000多个基因进行了测序分析,范科尼贫血(Fanconi Anemia)是一种由基因变异引发的遗传性贫血,它会导致骨髓障碍和癌症,许多患者在早年会发生急性骨髓性白血病。随后研究者鉴别出了引起疾病发生的相关基因突变位于ERCC4基因位点,而该基因和两种罕见的疾病-着色性干皮病和一种早衰直接相关,后者主要特点为对太阳光具有较高的敏感性,易发生皮肤癌。范科尼贫血其主要特点为进行性贫血、先天性畸形以及患口腔肿瘤和白血病风险升高。因此ERCC4基因和上述三种疾病直接相关。
研究者发现ERCC4基因参与了两种DNA的修复机制,DNA的修复机制是细胞维持基因组稳定性的一种方式,在两种修复系统之间的平衡就可以确定病人最容易感染哪种疾病。研究者Jordi Surralles指出,ERCC4基因是一个特例,因为很少有一个单独的基因可以参与两种生化代谢机制,同时可以引起三种不同疾病。
这项最新的研究发现或许可以帮助研究者们改善罕见疾病的诊断及遗传特性判断标准,而且为开发新型的治疗策略,比如基因疗法等方法提供新的思路。这项研究也帮助研究者理解了两种DNA的修复机制,其对于维持细胞中基因的稳定性,预防癌症发生非常重要。研究者还表示,这对于研究及理解基因ERCC4在乳腺癌以及卵巢癌的发病过程中也显得尤为重要。
原文链接:
Mutations in ERCC4, Encoding the DNA-Repair Endonuclease XPF, Cause Fanconi Anemia
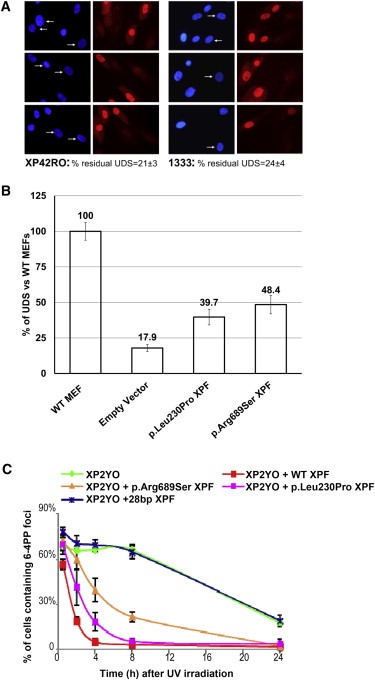
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare genomic instability disorder characterized by progressive bone marrow failure and predisposition to cancer. FA-associated gene products are involved in the repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICLs). Fifteen FA-associated genes have been identified, but the genetic basis in some individuals still remains unresolved. Here, we used whole-exome and Sanger sequencing on DNA of unclassified FA individuals and discovered biallelic germline mutations in ERCC4 (XPF), a structure-specific nuclease-encoding gene previously connected to xeroderma pigmentosum and segmental XFE progeroid syndrome. Genetic reversion and wild-type ERCC4 cDNA complemented the phenotype of the FA cell lines, providing genetic evidence that mutations in ERCC4 cause this FA subtype. Further biochemical and functional analysis demonstrated that the identified FA-causing ERCC4 mutations strongly disrupt the function of XPF in DNA ICL repair without severely compromising nucleotide excision repair. Our data show that depending on the type of ERCC4 mutation and the resulting balance between both DNA repair activities, individuals present with one of the three clinically distinct disorders, highlighting the multifunctional nature of the XPF endonuclease in genome stability and human disease.
关注转化医学网
【转化医学网 新浪微博:@转化医学网】
【转化医学网 公众微信账号:zhuanhuayixue】或扫描二维码关注微信

扫描微信二维码关注
来源:生物谷
 腾讯登录
腾讯登录
还没有人评论,赶快抢个沙发