Scientific Reports:研究人员发现杀死白血病细胞的新方法
| 导读 |
近日,邓迪大学研究人员发现了一种新的方法来杀死白血病患者的癌细胞,这可能有助开发出更安全的抗白血病药物。CLL是最常见的白血病,Sudhir Tauro博士领导的研究小组一直关注于慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL),特别关注于慢性淋巴细胞白血病对治疗药物Tenovin的反应。
Tenovin是数年前St Andrews和Dundee科学家共同开发的... |
近日,邓迪大学研究人员发现了一种新的方法来杀死白血病患者的癌细胞,这可能有助开发出更安全的抗白血病药物。CLL是最常见的白血病,Sudhir Tauro博士领导的研究小组一直关注于慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL),特别关注于慢性淋巴细胞白血病对治疗药物Tenovin的反应。
Tenovin是数年前St Andrews和Dundee科学家共同开发的触发其他类型肿瘤细胞死亡的药物,机制为增加细胞内p53蛋白的水平。
然而,博士Tauro和他的团队发现,当用Tenovin处理后,虽然CLL细胞出现死亡,但并没有表现出p53蛋白水平的变化。该研究结果公布在Scientific Reports杂志上。
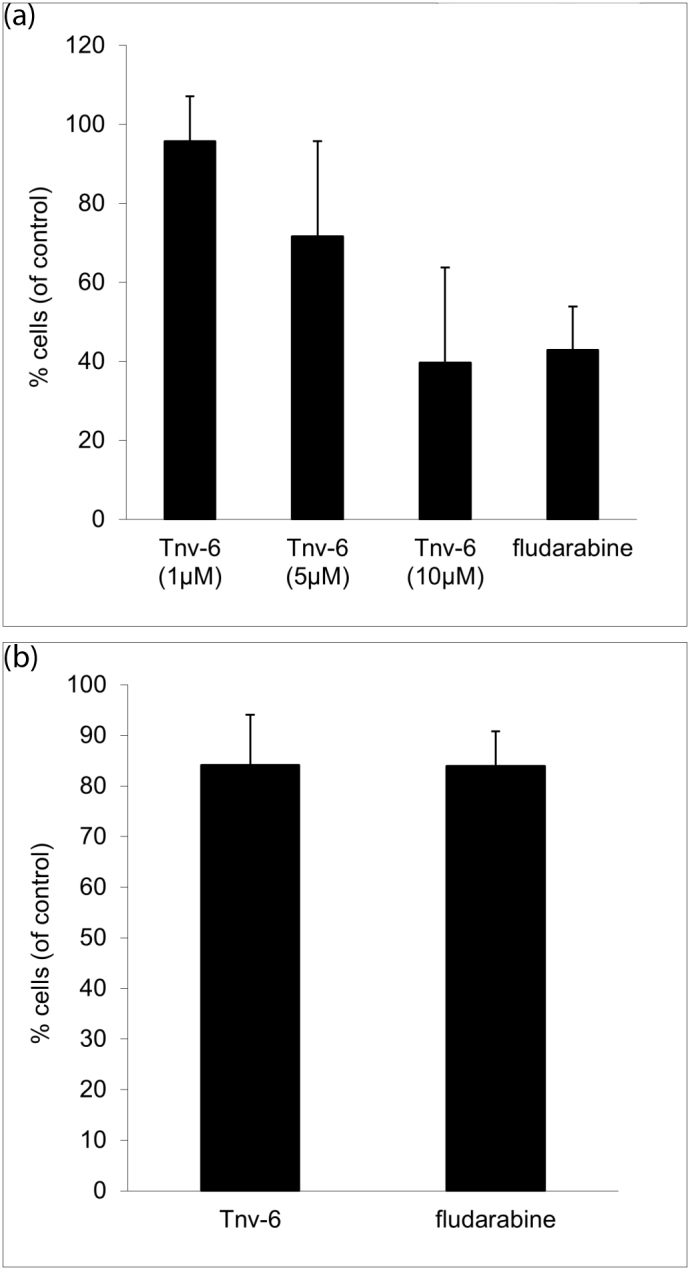
该研究小组发现,在白血病细胞中,Tenovin能够干扰白血病细胞的“自溶”过程,在应激过程中白血病细胞主要就是利用“自溶”过程来保护自己。Dundee癌症中心博Tauro士说:上述过程被称为自噬,自噬对所有细胞的生存是很重要的。
目前,抗白血病药物往往会导致毒性相关的问题,特别是在老年患者的治疗过程中,药物可能会影响正常血细胞计数。当反复使用时,往往有效性也会大打折扣。值得注意的是,虽然Tenovin能破坏白血病细胞这一过程,但Tenovin不影响正常的造血细胞。基于这些发现,研究人员现在可以利用这种差异,并开始开发更安全的抗白血病药物。
原文链接:
Dysregulation of autophagy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia with the small-molecule Sirtuin inhibitor Tenovin-6
Tenovin-6 (Tnv-6) is a bioactive small molecule with anti-neoplastic activity. Inhibition of the Sirtuin class of protein deacetylases with activation of p53 function is associated with the pro-apoptotic effects of Tnv-6 in many tumors. Here, we demonstrate that in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells, Tnv-6 causes non-genotoxic cytotoxicity, without adversely affecting human clonogenic hematopoietic progenitors in vitro, or murine hematopoiesis. Mechanistically, exposure of CLL cells to Tnv-6 did not induce cellular apoptosis or p53-pathway activity. Transcriptomic profiling identified a gene program influenced by Tnv-6 that included autophagy-lysosomal pathway genes. The dysregulation of autophagy was confirmed by changes in cellular ultrastructure and increases in the autophagy-regulatory proteins LC3 (LC3-II) and p62/Sequestosome. Adding bafilomycin-A1, an autophagy inhibitor to Tnv-6 containing cultures did not cause synergistic accumulation of LC3-II, suggesting inhibition of late-stage autophagy by Tnv-6. Thus, in CLL, the cytotoxic effects of Tnv-6 result from dysregulation of protective autophagy pathways.
来源:生物谷
 腾讯登录
腾讯登录
还没有人评论,赶快抢个沙发