Nature子刊:iPS重编程机制的新进展
| 导读 |
成熟细胞能够被重编程为多功能细胞,重新获得分裂并分化成为特定类型细胞的能力。这样的多功能细胞被称为诱导多功能干细胞(iPSC),是干细胞研究领域的重要里程碑,不过人们还并不完全了解重编程背后的许多生化过程。
已知表达O... |
成熟细胞能够被重编程为多功能细胞,重新获得分裂并分化成为特定类型细胞的能力。这样的多功能细胞被称为诱导多功能干细胞(iPSC),是干细胞研究领域的重要里程碑,不过人们还并不完全了解重编程背后的许多生化过程。
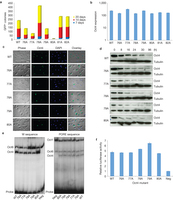
已知表达Oct4、Sox2、Klf4和c-Myc1, 2可以将已分化细胞重编程为多功能干细胞,其中Oct4在重编程过程中起着至关重要的作用,只有它不能被同家族的其他成员替代。欧洲分子生物学实验室EMBL和马普分子生物医学研究所的科学家们对此展开了研究,他们解析了Oct4特殊链接序列的3D结构,分析了该因子引发大量表观遗传学改变的机制。这项研究于二月四日发表在Nature Cell Biology杂志上,加深了人们对细胞重编程的了解,为其在再生医学和药物研发领域的医疗应用奠定了基础。
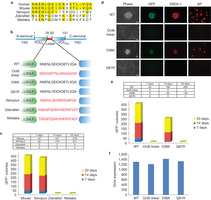
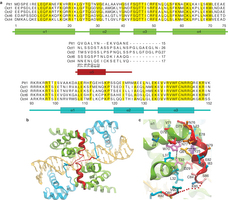
转录因子Oct4是与DNA结合的蛋白,控制着许多参与细胞重编程的基因。现在,研究人员用高强度的X射线,解析了Oct4的晶体结构,特别是Oct4两个DNA结合元件之间的链接序列。“我们在十多年前就注意到这个独特的链接区,因此我们非常高兴能够首次揭示这一区域在iPS重编程中的作用,”领导这项研究的Matthias Wilmanns说。
研究显示Oct4两个DNA结合域间的链接形成α-螺旋并且暴露在蛋白表面,这与链接区松散的Oct1不同。研究人员指出,这一链接区域负责招募其他关键蛋白到达Oct4所靶标的基因,没有它们iPS重编程就无法完成。
为验证这一理论,研究人员向Oct4链接区引入点突变,发现这只影响了Oct4的重编程活性,却没有影响它的其他基本特性。研究显示,Oct4的链接区域是蛋白相互作用的界面,负责招募关键表观遗传学调节子到Oct4靶标的基因。
“我们的研究展示了Oct4的独特结构及其对iPS重编程的重要性。这是了解细胞重编程机制的重要进步,这项发现有助于药物研发和组织工程领域的新应用。” 马普分子生物医学研究所的Hans Schöler说。
研究人员计划深入研究,揭示在多功能干细胞的重编程过程中,Oct4与其他相关蛋白元件一同作用的机制。
原文链接:
A unique Oct4 interface is crucial for reprogramming to pluripotency
Terminally differentiated cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotency by the forced expression of Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc1, 2. However, it remains unknown how this leads to the multitude of epigenetic changes observed during the reprogramming process. Interestingly, Oct4 is the only factor that cannot be replaced by other members of the same family to induce pluripotency3, 4, 5. To understand the unique role of Oct4 in reprogramming, we determined the structure of its POU domain bound to DNA. We show that the linker between the two DNA-binding domains is structured as an α-helix and exposed to the protein’s surface, in contrast to the unstructured linker of Oct1. Point mutations in this α-helix alter or abolish the reprogramming activity of Oct4, but do not affect its other fundamental properties. On the basis of mass spectrometry studies of the interactome of wild-type and mutant Oct4, we propose that the linker functions as a protein–protein interaction interface and plays a crucial role during reprogramming by recruiting key epigenetic players to Oct4 target genes. Thus, we provide molecular insights to explain how Oct4 contributes to the reprogramming process
来源:生物通
 腾讯登录
腾讯登录
还没有人评论,赶快抢个沙发